|
|
Control of Developmental Regulators by Polycomb in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Acknowledgements References |
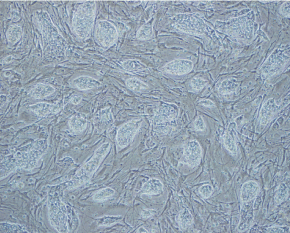
Human embryonic stem (ES) cells were obtained from WiCell (Madison, WI; NIH Code WA09) and grown according to the supplier’s recommendations. Briefly, passage 34 cells were grown in KO-DMEM medium supplemented with serum replacement, basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF), recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and a human plasma protein fraction. Detailed protocol information on human ES cell growth conditions and culture reagents are available at http://www.mcb.harvard.edu/melton/hues. In order to minimize any murine embryonic fibroblast (MEF) contribution in our analysis, H9 cells were cultured on a low density of irradiated MEFs (ICR MEFs) resulting in a ratio of approximately >8:1 H9 cell to MEF (Figure S1).
Figure S1. Human H9 ES cells cultured on a low density of irradiated murine embryonic fibroblasts.
Bright-field image of H9 cell culture. The culture of H9 on low-density MEFs had no adverse affects on cell morphology, growth rate, or undifferentiated status as determined by immunohistochemistry for pluripotency markers (e.g. Oct4, SSEA-3, Tra-1-60). In addition, H9 cells grown on a minimal feeder layer maintain the ability to generate derivates of ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm upon differentiation.
|
| YOUNG
LAB
Whitehead Institute 9 Cambridge Center Cambridge, MA 02142 [T] 617.258.5218 [F] 617.258.0376 CONTACT US |