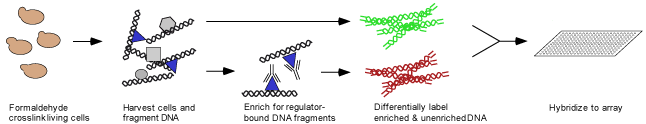
Technology - Location Analysis
Genome-wide location analysis was performed as previously described (Ren
et al., 2000), except that crosslinking time was reduced to 30 minutes and
high-resolution oligonucleotide arrays were used for hybridizations. Bound proteins
were formaldehyde-crosslinked to DNA in vivo, followed by cell lysis and sonication
to shear DNA. Crosslinked material was immunoprecipitated with the appropriate
antibody, followed by reversal of the crosslinks to separate DNA from protein
(Aparicio,
1999; Orlando
et al., 2000). Immunoprecipitated DNA and reference DNA were amplified and
differentially fluorescently labeled by ligation-mediated PCR. These samples
were hybridized to a microarray consisting of spotted PCR products representing
nearly all of the S.cerevisiae genome.
In analyzing histone modification, we find that an alternative experimental
design yielded improved results. Specifically, material immunoprecipitated with
antibodies directed against modified histones were compared to material immunoprecipitated
with antibodies directed against core histones. The results of both approaches
are analyzed with respect to transcriptional activity here.
Microarray design
The Agilent DNA microarray used here has 44,290 features consisting of 60-mer
oligonulceotide probes. The array covers 12 Mb of the yeast genome (85%), excluding
highly repetitive regions, with an average probe density of 266 bp. Intergenic
regions are represented by 14,256 probes and ORFs are represented by 27,185
probes. The remaining 2,849 control features included blank spots and probes
derived from Arabidopsis thaliana. The probe list for this array may
be found here.
